FROM EDITOR
PHARMACOEPIDEMIOLOGY
Objective. To conduct a pharmacoepidemiological and pharmacoeconomic analysis of specialized inpatient medical care provided to patients with metastatic melanoma (MM) in the Moscow Region during 2020–2022.
Materials and methods. A retrospective pharmacoepidemiological analysis of specialized inpatient medical care provided to patients with MM in Moscow Region during 2020–2022 was performed, followed by a cost analysis. The study analyzed the total number of patients receiving various drug therapy regimens with their main clinical characteristics (gender, age, diagnosis code), the total number of hospitalizations considering their structure (inpatient/day hospital), the average number of hospitalizations per patient, and the average length of hospital stay. The cost analysis examined both total costs and their structure across different drug regimens. The results were processed using Microsoft Excel 2019 and are presented as absolute values and percentages (%).
Results. This study examined 10,609 cases of specialized and primary specialized inpatient medical care provided to patients diagnosed with ICD-10 C43.0–43.9 in healthcare facilities of the Moscow Region from 2020 to 2022 (4,471 cases in 2020, 2,970 cases in 2021, and 3,168 cases in 2022). During the analysis period, the number of patients with MM receiving inpatient treatment decreased by 29 %, whereas the average number of hospitalizations per patient was 6.2 in 2020, 5.2 in 2021, and 6.3 in 2022. The hospitalization structure showed a trend toward decreasing the proportion of care provided in the 24-hour inpatient setting. The total costs of specialized medical care for patients with MM ranged from 1.8 billion rubles (2020) to 1.1 billion rubles (2022). In 2020, the three most demanded regimens by number of patients and hospitalizations were nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and dabrafenib + trametinib combination. This pattern persisted until 2021. In 2022, a shift in MM pharmacotherapy priorities was observed — alongside nivolumab and pembrolizumab regimens, prolgolimab became one of the most demanded treatments. These regimens were administered to more than 80 % of patients with MM at each time interval. Cost analysis revealed that in 2020, the same regimens that led in patient numbers also accounted for more than 95 % of total costs. In 2021 and 2022, the costliest regimens were those using nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and the combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab, accounting for more than 90 % of the costs. Drug therapy using pembrolizumab and nivolumab became the absolute leader both in patient numbers and costs throughout the entire analysis period, with nivolumab showing a gradual decrease in both patient numbers (1.7-fold) and cost levels (3.2-fold), while pembrolizumab showed the opposite trend —growth (1.5-fold and 1.9-fold, respectively).
Conclusions. The results of this analysis can contribute to further improvement of the regional medical care system for patients with MM, thereby enhancing the quality and accessibility of modern and highly effective pharmacotherapy approaches.
Objective. To conduct a pharmacoepidemiologic and pharmacoeconomic analysis of government procurement of drugs for the treatment of metastatic melanoma (MM) in Moscow region during 2020–2022, assessing the compliance of real clinical practice with current recommendations and identifying opportunities to optimize drug provision for patients.
Materials and methods. A retrospective pharmacoepidemiologic analysis of data on government procurement of key drugs used in the treatment of metastatic MM for the period 2020–2022 in Moscow region was performed, followed by a cost analysis. The analysis included 17 INNs: vemurafenib, vinblastine, dabrafenib, dacarbazine, imatinib, interferon alfa-2b, ipilimumab, carboplatin, cobimetinib, lomustine, nivolumab, paclitaxel, pembrolizumab, prolgolimab, temozolomide, trametinib, and cisplatin. The number of customers, trade names, dosage forms and packaging, number of packages purchased, cost per package, and total costs were analyzed. The average cost per 1 mg of active substance was separately evaluated over time. The results were processed using MS Excel 2019 and presented as absolute values and percentages.
Results. Data from the procurement information system (https://zakupki.gov.ru) for 2020–2022 were analyzed, covering 1,831 government procurements of 17 INNs used for MM treatment in Moscow region healthcare facilities (622 in 2020, 686 in 2021, 523 in 2022). Total expenditure for the 17 INNs amounted to 4.8 billion rubles for the entire 2020–2022 period (1.3 billion in 2020, 1.8 billion in 2021, 1.7 billion rubles in 2022), with an increase in expenditure of more than 30 %. The cost structure was dominated by 3 INNs throughout the analyzed period — dabrafenib, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab, accounting for an average of 76.5 % of all expenses. During 2020–2022, pembrolizumab was the absolute leader (accounting for 39.2 % of purchases in 2020, 33.3 % in 2021, and 35.2 % in 2022), with cost growth of 1.2 times. Regarding the average cost per 1 mg of active substance, the most expensive MM treatments were: ipilimumab, trametinib, pembrolizumab, prolgolimab, and nivolumab. Over the 3-year period, among these INNs, only ipilimumab showed an increase in the average cost per 1 mg (+18.6 %), while prolgolimab showed a significant decrease (–17.2 %). When comparing different healthcare settings, there is a clear trend toward decreasing numbers of patients receiving oral targeted therapies in inpatient settings, while in outpatient settings the number of patients significantly increases, especially evident for the combination of dabrafenib and trametinib.
Conclusions. Our study is the first example of a comprehensive pharmacoepidemiologic and pharmacoeconomic analysis covering various aspects of drug provision for patients with metastatic MM — government procurement, provision within preferential drug supply programs, and specialized medical care in hospital settings. The research results create an information base for making clinically and economically sound healthcare decisions, which can be used in developing regional oncology service programs, planning drug procurement, and improving the drug supply system for patients with metastatic MM.
Background. In pregnant women at high perinatal risk, irrational pharmacotherapy can lead to ineffective treatment, severe maternal and fetal complications, and increased healthcare costs. Adherence to evidence-based clinical guidelines is therefore critical for optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
Objective. To evaluate the pharmacotherapy regimens of pregnant women at high perinatal risk in Saratov and assess their compliance with clinical guidelines.
Methods. A retrospective pharmacoepidemiological study was conducted, analyzing 200 outpatient medical records of pregnant women at high perinatal risk. The analysis focused on the structure of prescribed drugs and their daily dosages relative to guideline recommendations.
Results. Polypharmacy (concurrent use of ≥5 drugs) was most prevalent in the third trimester (8.5% of patients). The most frequent drug combination was vitamin-mineral complexes with progesterone, prescribed to 11%, 10.5%, and 8.5% of patients in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively. Widespread non-compliance with guidelines was observed: potassium iodide was dosed inappropriately in 99%, 100%, and 97% of cases across the trimesters; folic acid dosage was incorrect in 70.5% of cases. Antihypertensive therapy was omitted in 57% of patients with arterial hypertension and 77% with gestational hypertension or hypertensive vegetative-vascular dystonia. Drug use was also frequently inconsistent with recommendations for dipyridamole (97% of cases), acetylsalicylic acid (33%), and anticoagulants for thromboembolic prophylaxis (86%).
Conclusion. Pharmacotherapy for pregnant women at high perinatal risk in this setting demonstrates significant non-adherence to clinical guidelines, potentially compromising treatment efficacy and safety. These findings underscore the need for enhanced monitoring of prescribing practices and interventions to improve physician adherence to established recommendations.
HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
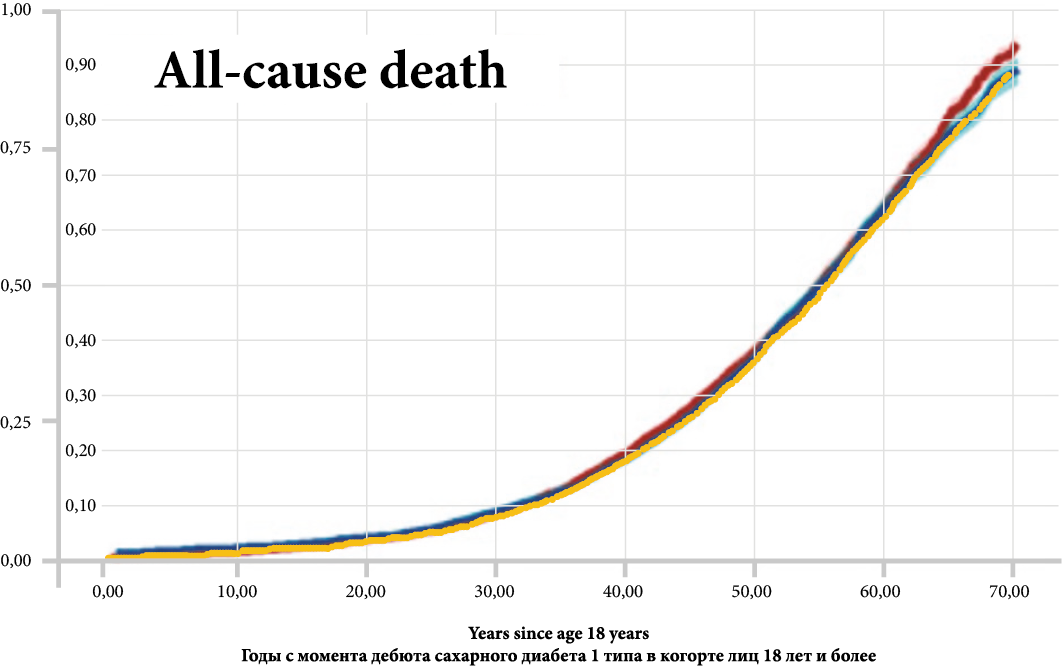
Background. Modeling of the socio-economic burden of diabetes mellitus type 1 (DM1T) in cohorts of children, adolescents, and adults was performed based on epidemiologic and calculated data for the first time in the local conditions. The specificity of the analysis is the calculation of the direct and indirect costs from social and government positions as well as the creation of the expenditure structure in each cohort of patients. Potential expenditures and their decreasing in patients 5–9 y. o. in case of illness delay have been evaluated on a 5‑year horizon.
Objective. The burden of DM1T evaluation in different cohorts divided by age and how it changes in the most sensitive group of patients (aged 5–9 y. o.).
Materials and methods Direct medical costs (DMC), indirect medical costs (IMC) and indirect costs (IC) in cohorts of kids (<15 y. o.), adolescents (15–18 y. o.) and adults were evaluated using the modeling method. DMC included: diagnostic and laboratory control, in- and out-patients’ treatment, rehabilitation, and treatment of complications. IMC was defined as the amount of pension payments due to early disability and benefits, means of individual mobility after amputation, payment for temporary disability due to hospitalization and outpatient treatment of disease and its complications, as well as for the care of a sick child of one parent. IC was defined as the loss of GDP. A total of 277 092 patients with DM1T were included in the analysis, 35 019 children and 13 012 adolescents. Diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, diabetic ketoacidosis, amputation, myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiac insufficiency, and severe hypoglycemia as well as their costs have been taken into calculation.
Results. In the children’s cohort, expenditures were 256 762 RUR/pts, and insulin cost was 40%; in the adolescent’s cohort, — 293 611 RUR/pts, insulins — 102 907 RUR/pts; in adults, — 1 910 569 RUR/pts, and DMC — 17% (from all cost), IMC — 728 225 RUR/pts., (38%), IC — 861 179 RUR/pts. (45%). Total costs in the kids’ cohort — 9.28 bln RUR, in adolescents — 3,9 bln RUR, in adults — 438,5 bln RUR. Common burden was 451,6 bln RUR, DMC — 17,9%, 57,8 bln RUR from that is cost of complications. The cost of insulin therapy was only 4% of the total burden. DMC is prevalence in kids and adolescents’ cohorts, including cost of complications (20–26% from all direct cost), in the same time IMC (more — in adults) — 170,4 bln RUR. IC in kids and adolescents — 4–5% only from total burden, in adults — 197,6 bln RUR (45%). The burden is going to decrease by 13% already in the first year in case of delay of an DM1T onset, and on 62% in case of delay on 5 years.
Conclusion. DM1T is a socially significant disease, the burden of which is determined in the group of children and adolescents with DMC, in adults — by an increasing proportion of IMC and IC especially. Delaying the onset of the disease in children, even by 1 year, saves DMC of the budget.
CLINICAL TRIALS
Background. The introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies in clinical trials (CTs) opens up new horizons for drug development, but it is associated with significant methodological and regulatory challenges. The gap between the speed of technological progress and its practical implementation necessitates the development of comprehensive approaches for the effective integration of AI into research practice.
Objective. To summarize and systematize the key areas of AI application at all stages of the clinical trial life cycle, identify existing barriers, and propose a comprehensive model to overcome them.
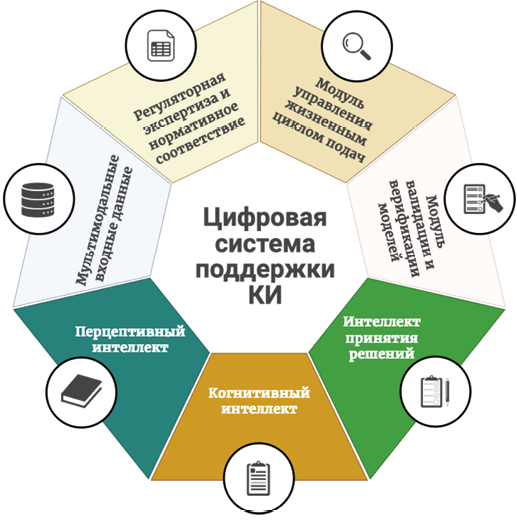
Materials and methods. A systematic analysis and generalization of data from current scientific publications, regulatory documents, and methodological recommendations on the use of AI in clinical trials was conducted (during 01.09.2019 по 28.08.2025 yy). The concept of a multilevel AI architecture, including perceptual, cognitive, and decision-making intelligence, was used as a basis for structuring the material.
Results. In the course of the analysis, the key areas of AI application were identified and characterized in detail: from the development of a study design and optimization of patient recruitment using digital twins to decentralized data monitoring and predictive analysis of adverse events. The main barriers that hinder the widespread adoption of AI have been identified: data quality and representativeness problems, model insufficient interpretability, lack of unified validation standards, and legal uncertainty. A multilevel model for AI integration is proposed, covering the technological, organizational, ethical, and regulatory aspects.
Conclusion. The full integration of AI into clinical trials can dramatically increase their effectiveness and reduce the time and cost of developing new drugs. We believe that overcoming the existing barriers requires coordinated efforts of the scientific community, regulatory authorities, and the pharmaceutical industry to create a single ecosystem that ensures the transparency, reliability, and ethics of the use of digital technologies.
DRUG SAFETY
Introduction. Patients with severe COVID-19 complicated by nosocomial pneumonia (NP) are often elderly with multimorbidity, necessitating polytherapy and carrying a high risk of drug interactions (DIs). Particular attention should be paid to DIs involving antibacterial drugs, which are widely used in the treatment of NP.
Objective. To conduct a retrospective pharmacotherapeutic analysis of drug therapy in an elderly patient with COVID-19 and NP to identify and assess the clinical risks of potentially significant DIs associated with antibacterial drugs.
Materials and methods. Based on the analysis of the medical history of an 81‑year-old female patient, a quantitative and qualitative assessment of the prescribed drugs was performed. The international database Drugs.com and the domestic system MedBaseGeotar (beta-version) were used to identify and rank DIs. Only clinically significant (category Major/Significant) DIs involving antibacterial drugs were analyzed.
Results. A total of 30 drugs were used during therapy (36 when considering components of combination drugs). The Drugs.com system did not reveal any clinically significant DIs among antibacterial agents. The domestic MedBaseGeotar system identified three significant DIs: linezolid + fentanyl (risk of serotonin syndrome), meropenem + linezolid and polymyxin B + meropenem (risk of pseudomembranous colitis and nephrotoxicity). Clinical analysis noted a synergistic increase in serum creatinine during the combination of polymyxin B and meropenem, indicating realized nephrotoxicity.
Conclusion. Despite pronounced polypharmacy, the number of identified clinically significant DIs was relatively small. The domestic MedBaseGeotar system demonstrated higher informativeness compared to the international counterpart for this clinical case. The obtained data emphasize the need for careful monitoring of patients with polypharmacy, using multiple systems for DI detection, and further improvement of domestic drug interaction databases.
Introduction. Pharmacovigilance is a scientific and practical activity focused on monitoring and studying the safety of medicinal products to prevent their adverse effects. Errors resulting from irrational drug prescribing are preventable. Reducing such prescription errors is a continuous process aimed at improving the quality of healthcare services. Errors occurring at the prescribing stage can be detected when drugs are dispensed in pharmacies.
Objective. To develop processes for improving the provision of pharmaceutical services to the population, considering the increasing prevalence of patient comorbidities.
Material and methods. The study employed general logical methods of scientific inquiry, structural-logical and empirical methods, generalization and extrapolation, recursion and computer modeling, as well as statistical analysis.
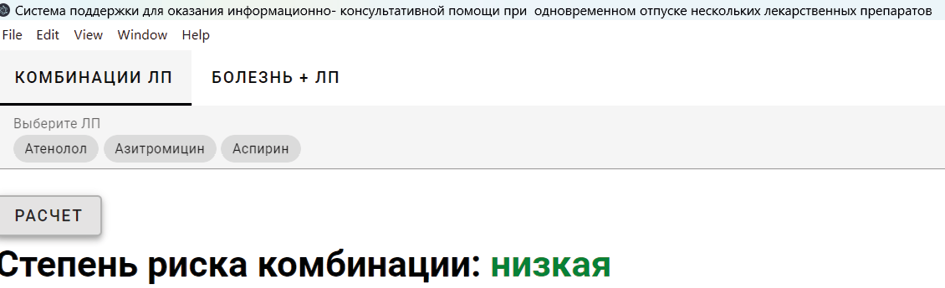
Results and discussion. Pharmaceutical counseling during drug dispensing is a key responsibility of pharmacists in providing pharmaceutical services. At this stage, pharmacists offer services in the form of counseling and information. As part of this research, a computer program titled «A Support System for Informational and Advisory Assistance in the Simultaneous Dispensing of Multiple Drugs» was developed. The program is designed to function as a decision support system for pharmacists, aiding in pharmaceutical counseling and information provision in complex cases involving the simultaneous dispensing of multiple drugs with potential adverse interactions. Testing of the program in a pharmacy setting demonstrated a 20% reduction in the time required for drug selection during pharmaceutical counseling.
Conclusion. An experimental evaluation of the program's effectiveness showed that its implementation into the practice of pharmaceutical information at the dispensing stage in pharmacy organizations can increase pharmacy revenue by up to 6%. Simultaneously, it addresses another identified issue — the lack of time for pharmacy staff to enhance their competencies in performing pharmacovigilance functions.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
This review analyzes modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of severe bronchial asthma (SBA), characterized by a transition to personalized medicine. The need to improve therapy for SBA is driven by its increasing prevalence and high resource consumption. This study examined the role of genetic polymorphisms in predisposition, disease course, and therapy response. Considerable attention is paid to pharmacogenetics, highlighting key genetic markers that influence the efficacy of basic bronchial asthma drugs (beta-agonists, inhaled corticosteroids, and leukotriene modifiers) and the possibility of personalizing the choice of biological therapy. A significant part of the review focused on monoclonal antibodies (omalizumab, mepolizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab, dupilumab, and tezepelumab), which represent a targeted approach to the treatment of SBA. The key predictors of treatment effectiveness (e. g., blood eosinophil level, IgE, FeNO, and exacerbation frequency) were analyzed for each group of biological drugs, and the importance of early initiation of therapy was emphasized to achieve maximum effect and prevent airway remodeling. Conclusion: The paradigm shift in SBA management through biological therapy, including achieving clinical remission and reducing the need for systemic corticosteroids, enables effective control in a significant proportion of patients with severe forms of the disease.
Introduction. Improving the efficiency and safety of pharmacotherapy in healthcare are priority tasks for healthcare systems. Irrational pharmacotherapy, polypharmacy, and adverse drug interactions typically lead to undesirable side effects, which not only reduces the efficacy and safety of treatment but also increases its cost. The selection of methods for assessing the quality of drug therapy prescribed to an individual patient, as well as the organization of quality control for pharmacotherapy in medical institutions, remain highly relevant.
Objective. To study the experience of using various methods for assessing the quality and safety of pharmacotherapy in the clinical practice of domestic and foreign healthcare systems.
Materials and methods. A review analysis of the use of methods for assessing the quality and safety of pharmacotherapy in domestic and international clinical practice was conducted based on a selection of publications identified through a keyword search. A list of the most frequently used methods for assessing the quality of pharmacotherapy was determined, including: the GTT method, Beers criteria, the GerontoNet scale, the STOPP/START criteria, and the Medication Appropriateness Index (MAI). Restrictive drug lists adopted in Sweden, France, Germany, and Turkey, which were developed using these methods to prevent the inappropriate use of medications, were also considered. Specialists widely use drug databases, such as Drug-drug interaction databases, to improve the quality of pharmacotherapy and prevent adverse drug interactions.
Conclusions. Currently, comprehensive approaches and methodologies for assessing the quality and safety of pharmacotherapy, suitable for regulatory purposes and widespread implementation, have not yet been fully established in many countries, including the domestic healthcare system. Previously, by Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia No. 494 dated October 22, 2003, "On Improving the Activities of Physicians — Clinical Pharmacologists," the "Form of Expert Assessment of the Quality of Pharmacotherapy" was adopted, which allows for an assessment of the quality of pharmacotherapy with a conclusion based on expert opinion. Modern evidence-based medicine approaches require a quantitative assessment of pharmacotherapy review results to enable an objective conclusion. In this regard, it is relevant to create an expert tool for assessing the quality and safety of pharmacotherapy based on the integrated use of existing assessment methods. This tool should be capable of determining compliance with: clinical guidelines, the clinical efficacy of drug therapy, rationality and safety indicators, including an assessment of the risks of adverse reactions.
Introduction. Severe burn injuries represent a critical medical condition associated with high mortality rates, primarily due to septic complications. Modern combustiology requires integrated approaches aimed at improving survival and reducing infection risks.
Objective. To analyze contemporary strategies and innovations in the treatment of patients with severe burns, focusing on systemic therapy and local wound management.
Materials and methods. A literature review of recent scientific publications and clinical studies was conducted, covering aspects of antibacterial therapy, immunomodulation, and the use of advanced wound dressings and skin substitutes.
Results. Key directions in managing severe burns include early systemic antibiotic therapy targeting resistant pathogens (e. g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, MRSA) and selective intestinal decontamination to prevent bacterial translocation. Immunomodulation with immunoglobulins and colony-stimulating factors enhances host defense mechanisms. Local treatment benefits from innovative methods such as silver-based antimicrobial dressings, bioengineered skin substitutes, fish skin grafts, and techniques like hydrosurgical debridement, negative pressure wound therapy, and photodynamic therapy. These approaches collectively accelerate wound healing, reduce bacterial load, and minimize scarring.
Conclusion. A comprehensive treatment strategy, combining early antibiotic therapy, intestinal decontamination, immunomodulation, and advanced local wound care, significantly improves outcomes for patients with severe burns. Future perspectives involve the further development of cell-based therapies and regenerative medicine to enhance skin recovery.
BIOMEDICAL ETHICS
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being actively integrated into the drug development process, significantly accelerating it and reducing the costs of creating new therapeutic agents. This article examines key areas of AI application in the pharmaceutical industry, including molecular structure prediction, virtual compound screening, optimization of clinical trials, and personalized medicine. Special attention is paid to the ethical issues arising from the use of AI, such as algorithm transparency, accountability for errors, data privacy, technology accessibility, and regulatory challenges. The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for managing large multi-modal models in healthcare are analyzed. The article emphasizes the need to strike a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility, as well as to develop a regulatory framework for the safe and effective use of AI in medicine.
INTERNAL MEDICINE
Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a group of inflammatory disorders characterized by the involvement of axial and peripheral joints, as well as systemic manifestations. Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are a leading cause of mortality in patients with axSpA, and anti-inflammatory therapy with NSAIDs may further increase cardiovascular risk (CVR). While conventional CVR factors are well-established, a comprehensive CVR assessment in axSpA requires consideration of disease-specific features that complicate risk management. The COMOSPA study indicated that the association of SpA with psoriasis elevates CVR, particularly in cases with peripheral joint involvement. Regarding radiographic progression, a relationship was demonstrated between the mSASSS index and both arterial hypertension (AH) and CVR, whereas the BASRI was not associated with CVR. Studies on the impact of disease activity have shown that ineffective treatment and persistent inflammation are linked to increased AH and CVR. Conversely, NSAID therapy, by reducing disease activity and improving spinal mobility, was associated with lower CVR. Furthermore, a cohort of patients with "difficult-to-treat" axial spondyloarthritis demonstrated higher CVR, underscoring the importance of achieving remission or low disease activity for risk reduction. Persistent structural damage observed radiographically, in conjunction with elevated C-reactive protein and increased carotid intima-media thickness, was associated with higher CVR. Critically, studies have confirmed an increased incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events, such as acute coronary syndrome and stroke, in axSpA patients. In conclusion, current evidence confirms the necessity of achieving treatment targets through effective therapy to reduce mortality in patients with axSpA and comorbid cardiovascular pathology.
PALLIATIVE CARE
Patients with malignant brain tumors and brain metastases suffer from severe symptoms throughout the course of their disease, which requires special attention and comprehensive care to maintain their quality of life. This article provides a literature review, with an emphasis on the practical aspects of controlling the most common and disabling symptoms. Four main topics are discussed: symptom control, caregiver`s needs, palliative care during active cancer treatment, and end of life care. New data on the prevention of neurocognitive deficits through improved radiotherapy techniques and the choice of anticonvulsants for patients with seizure syndrome are presented. The main therapeutic options for managing weakness, neurocognitive decline, headache, and other types of pain are described, along with the current limitations of these treatments. The strategy for using opioids in this patient group is also discussed. The development and implementation of advance care planning programs can help ensure that care is aligned with the needs of patients and caregivers, which may reduce the volume of inpatient care and avoid unnecessary aggressive treatment at the end of life. The integration of palliative care into the healthcare system for patients with brain tumors is a paramount. There is a need to establish specialized palliative care services for this patient group and to provide targeted training for specialists. It is necessary to develop practical supportive and palliative care guidelines for patients with brain tumors, including end of life care.
ISSN 2618-8473 (Online)