FROM EDITOR
PHARMACOEPIDEMIOLOGY
Relevance. The treatment of moderate and severe psoriasis poses significant challenges in clinical practice. This article is devoted to the analysis of real-world clinical practice in the treatment of plaque psoriasis, factors causing relapses of plaque psoriasis, the prevalence of anxiety and depressive disorders, and the assessment of the quality of life of patients with psoriasis using various systemic medications among patients who were observed in dermatovenereological dispensaries of the Central Federal District during the period 2022–2023.
Objectives. To determine the optimal drug therapy for patients with plaque psoriasis based on comprehensive pharmacoepidemiological, clinical, compliance, and medication adherence assessments.
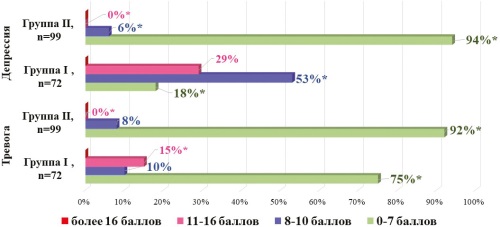
Materials and methods. Retrospective comparative analysis of the medical records of 336 patients with plaque psoriasis (L40.0), moderate and severe. Two comparison groups: Group I — 166 patients receiving methotrexate and Group II — 170 patients receiving genetically engineered drugs. Patients were surveyed by physicians to confirm their therapy compliance. The levels of anxiety and depression were assessed using the HADS scale, and quality of life was assessed using the dermatological quality of life index — DLQI.
Results. The highest rate of adherence to therapy (>80%) was recorded in the group of patients undergoing therapy with genetically engineered drugs and who had a high level of anxiety (r=0.202, p<0.05). In the group of patients with average adherence to the applied genetic engineering therapy (30–80%), a higher level of anxiety was associated with reduced adherence to treatment (r=–0.202, p<0.05). Average adherence to methotrexate (r =–0.249, p<0.05).
Conclusions. An increased level of anxiety in patients undergoing therapy with genetically engineered drugs increased their adherence to treatment (r=0.202, p<0.05). The worse the quality of life of patients undergoing therapy with genetically engineered drugs, the less adherence.
QUALITY OF LIFE
To date, there are no specific scales in the Russian Federation for the comprehensive assessment of patient satisfaction and experience of outpatient medical care.
Objective. To validate the previously translated Norwegian "Patient Experience Questionnaire" (PEQ), a validated patientreported experience measure (PREM) for outpatients.
Materials and methods. Patients aged over 18 years were invited to complete the questionnaire within 24 h after visiting a physician by clicking on a link in the QR [quick response] code printed on the medical report. The construct, discriminant validity, and reliability of individual questions, domains, and the entire questionnaire were analyzed.
Results. A total of 452 patients (47.3% male, median age 55 [38–68] years) completed the questionnaire. Less than 18% of the responses were missing. These responses were considered "missing at random". Most patients in this cohort had higher education (67.7%), were married (58%), and were seen by a female physician (91.4%). In confirmatory factor analysis, the factor loadings of the questions were all above 0.6 units, and the reliability of each question, individual scales, and the entire questionnaire was above 0.8 units. The overall questionnaire model met all the goodness-of-fit criteria.
Conclusions. The construct and discriminant validity of the previously translated into Russian language Patient Experience Questionnaire, has been confirmed. This PREM is proposed to be used in routine clinical practice and scientific studies under the name "RuPEQ".
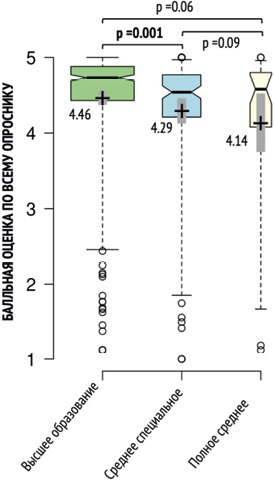
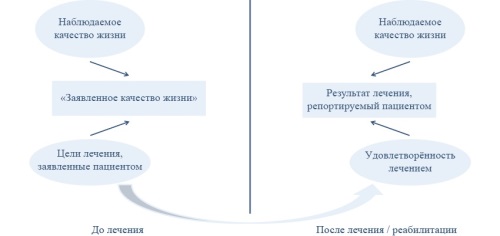
In modern patient-oriented medical care, quality of life is an important criterion for a comprehensive assessment of the patient's health and evaluation of treatment effectiveness. This article is devoted to the current methodological issues of assessing quality of life and other patient-reported outcomes (PRO) and attempts to reveal the difficulties of interpreting PRO data obtained in real-world clinical practice. A new concept for identifying significant changes in the patient's general health condition in clinical practice is presented, and a new model of quality of life outcomes before and after treatment is considered. The concepts of “declared quality of life”, “index of achieved quality of life” and “declared clinical effect” have been declared. Assessment of the declared quality of life of the patient and determination of the index of the achieved quality of life can be used for practical purposes to implement the principle of patient-oriented care in clinical practice.
PHARMACOVILIGANCE
Relevance. Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are serious adverse drug reactions (ADRs) associated with drug use. Knowledge of drug triggers is important for ADR prevention.
Objective. To study the structure of anti-infective drugs that cause the development of SJS and TEN.
Methods. We studied spontaneous reports (SRs) submitted to the Russian National Pharmacovigilance database from 01.04.2019 to 31.12.2023. SRs about the development of SJS or TEN were included. Suspected drugs in group J according to the ATC classification were analyzed.
Results. Among the 170 included SRs, anti-infectives were noted as suspects in 69, and the total number of drugs was 103. 75 drugs were antibacterial (beta-lactams were leading, n = 46), and 21 were antiviral agents.
Conclusion. In terms of the structure of anti-infective drug triggers, 72.8% were antibacterial drugs and 20.4% were antiviral agents.
Relevance. Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions that can be induced by drugs and are particularly severe in children.
Objective. To study the structure of antibacterial drugs (ABs) involved in the development of SJS and TEN in pediatric populations.
Methods. Retrospective pharmacoepidemiologic study of spontaneous reports (SRs) entered into the Russian National Pharmacovigilance database during the period 01.04.2019 – 31.12.2023.
Results. The majority of suspected drugs were β-lactams (76.0%), with penicillin accounting for 47.4% and cephalosporins — for 52.6%. Amphenicols (12.0%), macrolides (8.0%), and fluoroquinolones (4.0%) were less frequently reported.
Conclusion. The most common group of ABs that induce SJS and TEN in children is the group of β-lactam antibiotics.
Introduction. Risk of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) is a serious issue in pharmacotherapy and a major public health concern. Safety signal detection during the post-marketing phase is one of the most important goals of drug safety surveillance. Spontaneous reporting systems (SRS) are still widely used to identify safety signals based on real-world data. Various data mining statistical methods have been developed for this purpose, and they are classified into frequentist and Bayesian approaches. Statistical methods can also be used for the analysis of patient-related risk factors (demographic characteristics, concomitant diseases or medications). Identification of patients at high ADR risk is important for personalized pharmacotherapy.
Objective. To present and review issues and features of the statistical methods for SRS data, developed by other authors and published in the literature, this tool may be useful for appropriate statistical analysis and accurate interpretation of passive surveillance data.
Methods. In this paper, we present the known and commonly used frequentist or classical methods for correct statistical analysis of spontaneous reports. These methods for signal detection and their modification for drug-host factor interaction analysis are relatively easy to understand, interpret, and compute based on the contingency 2x2 tables: reporting odds ratio (ROR), proportional reporting ratio (PRR), and normal approximation test. Different approaches to the multiple comparison problem in passive safety surveillance settings were also discussed.
Results. As an example, the aforementioned methods were applied to analyze sex disparities in liver toxicity based on the spontaneous reports extracted from the Russian National Pharmacovigilance database. The tests identified drugs for which liver toxicity demonstrates significant disproportionality regarding sex compared with other AEs. The results of all statistical methods were similar.
Conclusions. Although spontaneous report databases are subject to numerous potential sources of bias and well-known limitations, these large-scale databases remain a widely used, effective, and relatively inexpensive approach for post-marketed drug surveillance. With the use of correct statistical methods, spontaneous reporting databases can provide valuable information for hypothesis generation, which should be investigated further, as well as essential data on the evaluation of risk factors and risk populations.
PHARMACOGENETICS
Relevance. The advantages of using clopidogrel for the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases have been demonstrated in many studies. However, the risk of clinically significant bleeding is increased when clopidogrel is used in combination with other drugs.
Objective. To investigate the possible relationship between the carriage of CYP2C19 loss-of-function and gain-of-function alleles and bleeding events in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) ± atrial fibrillation (AF) receiving dual antithrombotic therapy with clopidogrel after acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Materials and methods. A total of 150 patients (median age 65 [60,75;73] years) were studied, including 77 patients with CHD without AF taking clopidogrel + acetylsalicylic acid; and 73 patients with CHD and AF taking clopidogrel + rivaroxaban or apixaban. DNA samples obtained from all patients were genotyped for CYP2C19 rs4244285, rs4986893, and rs12248560. The follow-up period was 16 weeks ± 1 days. Information about bleeding events was obtained using the MCMDM-1 questionnaire.
Results. Bleeding occurred in 26 (17.3%) patients. The most common bleeding events were nosebleeds (42.3%), bruises (30.8%), and oral bleeding (26.9%). Among patients with bleeding events compared with those who did not, carriers of the rs12248560 (CYP2C19*17) TT genotype were significantly more common — 19.2% and 3.2%, respectively (p = 0.008). A similar result was obtained in the CHD group without AF (21.4% vs. 3.2%, respectively, p = 0.039). Among patients in the presence of bleeding, ultrarapid metabolizers (*17/*17) were administered significantly more frequently than those without bleeding (p=0.008).
Conclusion. Carriage of the rs12248560 (*17) TT genotype and ultrarapid metabolizers (*17/*17) phenotype were associated with hemorrhagic events in patients with ACS receiving dual antithrombotic therapy with clopidogrel.
INTERNAL MEDICINE
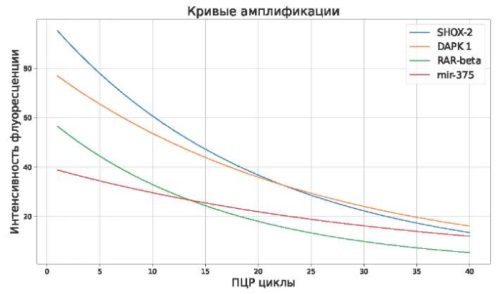
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by clinical manifestations, including proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, and edema. Hydrothorax is a rare but serious complication caused by enhanced fluid exudation due to hypoalbuminemia and changes in capillary permeability. In this study, the methylation of the SHOX-2, DAPK1, RAR-beta, and mir-37 genes was assessed in 35 patients with nephrotic syndrome and hydrothorax using DNA extracted from pleural fluid and urine. Methylation was determined using real-time PCR. The PCR results showed no methylation of SHOX-2, RAR-beta, DAPK1, or Mir-375. The amplification curves show an exponential increase in the signal and a stable plateau, indicating successful DNA amplification. The absence of methylation confirmed the high specificity of the method for detecting unmethylated sequences. These results highlight the need for further research to understand the epigenetic mechanisms of gene expression and to develop new therapeutic approaches aimed at modulating DNA methylation and restoring normal gene regulation.
Relevance. Eliminating the hepatitis C virus is one of the main tasks for infectious disease specialists.
Objective. To evaluate the efficacy and safety of therapy for chronic hepatitis C (HCV) with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (GP) in patients with concomitant diseases.
Methods. The results of HCV therapy in 153 patients from 4 groups were analyzed: those without concomitant diseases, with hypertension (GB), with GB and diabetes mellitus (DM), and with cirrhosis of the liver (CL).
Results. There were no differences in the effectiveness of HCV treatment between the patient groups. In patients with DM, blood glucose levels decreased by 6.3% after 2 months of HCV therapy.
Conclusion. HCG therapy with GP is effective in patients without concomitant diseases, such as GB, DM, and compensated CL. Patients with diabetes after HCV treatment should consult an endocrinologist to correct hypoglycemic therapy.
Relevance. The clinical course, treatment approaches, and outcomes of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) often depend on microcirculatory disorders. The significant prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in the population determines the frequency of CAP. Study of the pathogenetic basis of the combined course of CAP in individuals with GERD, incl. microcirculation systems, can target correction paths and increase the effectiveness of therapy.
Objective. To identify indicators of systemic inflammation and macrohemodynamics in patients with CAP combined with GERD.
Material and methods. A total of 123 patients were under observation, incl. with mild CAP without signs of GERD (group I) — 38, with CAP and GERD — 49 (group 2), and 36 patients with GERD without CAP — group 3. In all patients with CAP, along with traditional studies, the concentrations of C-reactive protein (CRP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) were determined in the blood, and echocardioscopy (EchoCS) was performed to determine the end systolic (ES) and diastolic (ED) volumes of the left ventricle (LV) and right ventricles (RV), blood flow velocity at the level of the pulmonary artery (Vmax PA), pressure gradients ΔPmax at the level of the tricuspid valve (TV), PA, and LV isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT). Control values for indicators were obtained from 34 practically healthy donors.
Results. In all patients with CAP, at the beginning of therapy, intoxication and respiratory syndromes were observed, and pneumonia was diagnosed on an X-ray. Patients in groups II and III had characteristic symptoms of GERD. Blood tests revealed leukocytosis in all patients with CAP. The initial CRP concentration in group 1 was 5.2, group 2 — 7.7, group 3 — 1.2 times higher than normal. The initial concentration of BNP in all groups did not differ from the control. By discharge, CRP levels in all patients had decreased: however, in group II, they remained higher than in healthy people (2.6 times (p < 0.05) and higher than in group I, 1.3 times (p < 0.05). Before discharge, the BNP level in group II increased by 1.2 times compared with baseline in group I, in healthy individuals, and in group III. When analyzing the EchoCS indicators in group II patients, a significant increase in the initial indicators of LV EDV and LV ESV and decrease in EF and IVRT were observed. After treatment, no significant dynamics of volume and velocity parameters were observed in patients in group II; in patients in group I, pressure gradients at the TC and PA levels remained slightly reduced.
Conclusions. An increase in CRP levels in patients with GERD characterizes low-intensity inflammation, which potentiates systemic inflammation in patients with CAP combined with GERD and is accompanied by an increase in BNP.
DRUGS UTILIZATION RESEARCH
Actuality. Antibiotic resistance includes the unjustified use of topical antibacterial agents.
Objective. To study the frequency of topical and systemic antibacterial drugs among adults with symptoms of otorhinolaryngological diseases over the past 6 months and the role of physicians in prescribing antibacterial drugs.
Methods: online questioning of adults. The data from a survey of 111 respondents aged over 18 years were analyzed. A group (61 out of 111) of respondents (54.96%) experiencing symptoms of otorhinolaryngological diseases and using medications 6 months before the survey was conducted was identified.
Results: 31.15% of respondents took systemic antibiotics. Of all respondents who received a systemic antibacterial drug, only 14 out of 19 (73.68%) took it as prescribed by a physician and 1 (2.38%) was prescribed by a pharmacist. At the same time, the respondents used all topical antibacterial drugs — 4 cases (6.6%) without the recommendation of a physician or pharmacist.
Conclusion. The prevalence of topical antibacterial drugs for the treatment of upper respiratory tract diseases among the study population was low, but the frequency of their use without the appointment of a specialist was high.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
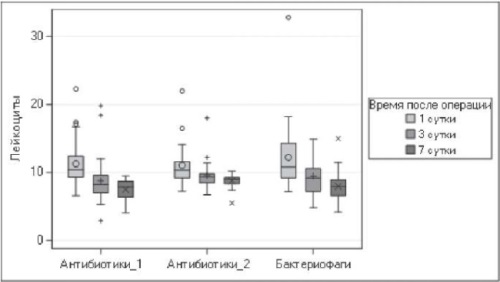
Relevance. Given the growing antibiotic resistance of pathogens of urologic infection to antimicrobial drugs, one of the urgent problems is the search for alternative methods of antimicrobial prevention of infectious and inflammatory complications after surgical interventions, as well as an adequate therapy regimen during the postoperative period. Bacteriophage preparation is an alternative method for the treatment and prevention of infectious and inflammatory urological diseases.
Objective. To determine an effective method for preoperative antimicrobial prevention of infectious and inflammatory complications in patients with kidney stones subjected to percutaneous nephrolithotripsy (PNLT).
Methods. The study included 90 patients with coralloid or multiple large kidney stones who underwent PNLT. Before PNLT, all patients underwent bacteriological urinalysis in order to determine sensitivity not only to antibiotics and bacteriophage preparations. Urine sampling was performed for further microbiological cultural examination during renal pelvic puncture on the 3rd and 7th days after PNLT. Depending on the technique of perioperative prophylaxis, three groups of 30 were formed. Group 1 patients were intravenously injected with 1000 mg of ciprofloxacin throughout the operation and then intravenously dipped with 1000 mg once a day for 3–5 days. Group 2 received intramuscular cefotaxime + sulbactam (1.0+0.5) twice a day 2 h before surgery intramuscularly once. In group 3, patients received oral mycobacteriophage 40 ml polyvalent purified orally 1 h before surgery and 40 ml orally 3 times a day for 3–5 days after surgery.
Results. In all three groups, the development of infectious complications in patients was assessed: acute pyelonephritis, systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome (SERS) or urosepsis. No serious infectious or inflammatory complications were observed in any group during the early postoperative period. The development of CVD after PNLT was noted on the 1st–3rd postoperative day (in 26.6 %, 20 and 20 % of patients of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd groups, respectively). However, on the 4th–7th day after PNLT, normal blood parameters (leukocytes, rod-shaped neutrophils), temperature, and general well-being were noted.
Conclusion. The same effectiveness of different antimicrobial regimens for preventing infectious and inflammatory complications after PNLT was similar. Bacteriophage preparations are effective and can prevent infectious and inflammatory complications following PNLT. The development of CVD after PNLT on the 1st–3rd day after surgery cannot be correlated only with the antimicrobial drugs used and the method of their administration (intravenously, intramuscularly and orally). Most likely, the development of CVD is associated with operational injury.
Improvement of the clinical outcomes of newborns with hospital-acquired infections requires microbiological monitoring to ensure timely initiation of appropriate empirical therapy. In our study we investigated the patterns of pathogens responsible for hospital-acquired infections in neonatal intensive care units and assessed the levels of antibiotic resistance among these pathogens. The study included 4,891 samples from newborns. Gram — positive microflora was found in 55.9% of the samples and gram-negative — in 44.1%. The antibiotic resistance profile revealed high resistance to penicillin-based antibiotics among staphylococci. Gram-negative microorganisms remained sensitive to most antibacterial drugs.
ISSN 2618-8473 (Online)