FROM EDITOR
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The article presents the results of clinical studies of amisulpride use in schizophrenia.
The aim of the work is to analyze the use of amisulpride in various forms of schizophrenia from the standpoint of efficacy and safety of use based on the results of clinical studies published in the scientific literature.
Amisulpride is an atypical antipsychotic with a unique receptor profile and a number of unusual pharmacological properties from other known atypical antipsychotics (in particular, it is a partial 5HT4-agonist, a partial GHB receptor agonist, a potent 5HT7-receptor antagonist). It has antidepressant, anxiolytic, analgesic and antiemetic activity, has a low probability of extrapyramidal adverse events and is highly effective in eliminating negative symptoms, cognitive and depressive disorders in schizophrenia and other psychoses. There is evidence of the effectiveness of amisulpride in relation to aggression, hostility, anxiety symptoms often observed in acute exacerbation of schizophrenic psychosis, as well as in affective disorders (major depressive episode, dysthymia, mania). Amisulpride has also demonstrated effectiveness in resistance to other antipsychotics. When used in combination with clozapine, it not only enhances the antipsychotic effect of clozapine, but also reduces hypersalivation caused by clozapine. According to the results of the presented clinical studies, the administration of amisulpride has a positive effect on both the positive symptoms and the negative manifestations of schizophrenia. The safety profile of amisulpride is unique in comparison with both classical and atypical antipsychotics. The low degree of biotransformation, the absence of active metabolites and predominant renal excretion make it possible to prescribe the drug even to patients with impaired liver function and elderly patients. Amisulpride does not interact with any medications, which is also a big advantage of the drug. A number of studies report that when taking amisulpride at a dose of up to 800 mg, extrapyramidal disorders are practically not recorded. Unlike most atypical antipsychotics, amisulpride has minimal ability to cause weight gain.
HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
Relevance. The anti-smoking policy in Russia has reduced the proportion of smokers to 30.7 %; however, about a third of smokers are not ready to quit. Underestimating the complexity of completely quitting smoking is a serious barrier to improving the health of the population. In recent years, sufficient data has accumulated that tobacco heating systems (THS) are less harmful to health and are quite an effective means of quitting smoking.
The objective of this study was to model the potential effects of all smokers switching to the use of THS.
The effect was considered as a decrease in the number of fatalities when using alternative nicotine delivery systems ANDS, compared with the mortality associated with smoking.
Methodology. The modeling compared the "zero" scenario with the "alternative" one. The "zero scenario" is the current situation with smoking prevalence, the "alternative scenario" assumed that all smokers completely switch to THS, and the reduction in health harm corresponds to the level of reduction in biomarkers of potential harmful effects of tobacco combustion products by 16-49 % for five of the 8 endpoints based on data from available studies.
Results. The transition of men from cigarette smoking to THS at the age of 35-59 years will save 39,102 lives (19.1 % of tobacco-associated mortality) and 1.3 million DALY years or 27.7 % of the losses that accompany cigarette smoking. In women aged 35-59 years, 3,815 deaths (4.1 %) are potentially prevented and 822 thousand DALY years are saved or a reduction in losses by 15.7 %. If we take into account the reduction in toxicity from the use of ANDS at 49 % and recalculate it for the entire population of smokers, the transition to ANDS can have a significant demographic effect in terms of reducing mortality, primarily in active working ages; the epidemiological gain in per capita GDP metrics could reach 1.5 trillion rubles in 2022.
Conclusions. The demonstrated potential reduction in health harm and the significant demographic effect in terms of mortality reduction when using electronic heated tobacco systems may serve as sufficiently strong arguments that should be taken into account when developing a regulatory framework for such electronic devices.
Relevance. Аntimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery (APS) is an important component of strategic healthcare programs aimed at reducing antibiotic resistance. The use of modern APS techniques also reduces the cost of prevention and treatment of surgical infection. However, the actual clinical practice of APS at the present time often differs from the scientifically based one, there is a suboptimal, excessive prescription of antibacterial agents. The introduction of APS using a Medical Decision Support System (DSS) can increase doctors' commitment to following modern medical technology.
Objective. To develop and implement a APS protocol for a multidisciplinary emergency hospital. To develop and implement a mobile application, a chatbot for choosing a decision on the mode of perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis.
Methods. Clinical and economic assessment of the "cost of illness" in the emergency department of surgical departments. Literary — an overview of regulatory documents as the basis of the APS protocol. Python programming method, digital application development. Development taking into account State industry standard R 71671-2024 "Medical decision support systems using artificial intelligence". Administrative — issuing orders and orders for the medical institution on the procedure for implementing the protocol, monitoring compliance with the protocol.
Results. A local APS protocol has been developed. Based on the APS protocol, standard solutions for choosing the APS method have been compiled. Applications (Telegram chatbots) have been developed to facilitate this choice for the doctor who decides on the APS regime. It has been established that the commitment to the implementation of the PAP protocol continues to grow. This may be due to the absence of an increase in cases of infection of the surgical wound, despite a multiple decrease in the use of antimicrobial agents. The visibility and convenience of using APS mode selection algorithms using digital technology are also revealed.
Conclusions. The implementation of the local protocol is effectively carried out using digital technologies, a system for supporting medical decision-making using artificial intelligence. The implementation of this APS protocol has made it possible to achieve significant cost reductions while maintaining the effectiveness of antimicrobial prophylaxis.
Aim. This study aimed to analyze the budget impact of mosunetuzumab use in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in the third and subsequent lines of therapy.
Materials and methods. Budget impact analysis, sensitivity analysis.
Results. The target population size was 340 people. Analysis of the costs of drug therapy for the third and subsequent lines demonstrated a wide range of costs: the maximum costs are associated with the use of mosunetuzumab (RUB 6,296,060.33, 8 cycles and RUB 11,906,411.12, 17 cycles), and the minimum costs are associated with the use of the GDP regimen without rituximab (RUB 31,390.80). The total costs for 1 year of modeling the current practice for all types of therapy amounted to RUB 891,446,565.79. In current practice, the main share of costs is attributed to the drug duvelisib (47.4 %), followed by the regimen ibrutinib+/-R (25.1 %) and R-B (6.1 %). More than 70 % of the current practice costs are spent on drugs that do not have an official indication for use. The total cost of 1 year of modeling amounted to RUB 693,639,708.26. Over the specified modeling period, the main share of costs was attributed to the following regimens: ibrutinib+/-R (32.3 %) and mosunetuzumab monotherapy (27.2 %). Budget impact analysis demonstrated that the use of mosunetuzumab will save 22.2 % or RUB 197,806,857.54 over 1 year and will allow for additional treatment with mosunetuzumab to 31 new patients. Sensitivity analysis of the budget impact analysis results demonstrated that the model is sustainable to changes in all initial parameters, even within the proposed option of transferring all patients from duvelisib to mosunetuzumab monotherapy will lead to a savings in current costs (2.9 %).
Conclusions. The use of mosunetuzumab as a 3rd and subsequent line therapy in adult patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma is an economically feasible approach within the Russian healthcare framework.
DRUG SAFETY
Relevance. Prenatal exposure to medicines with a teratogenic risk and the prevention of such exposure is an important clinical and public health issue. The first priority for the safe use of medicines, both during pregnancy and by women of reproductive age, is to know the teratogenic risk and to include it in the primary source of information.
Objective. To conduct a systematic literature review to identify and compare the results of drug safety studies in pregnancy based on data from officially recognised information documents.
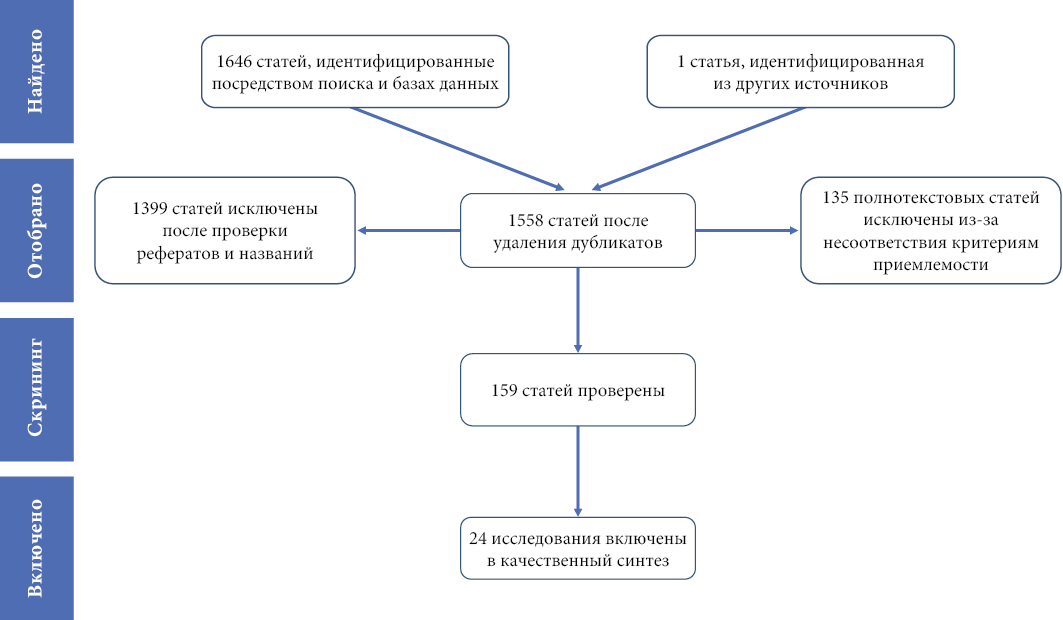
Material and methods. Literature searches were conducted in the electronic databases MEDLINE/PubMed from 1 January 2000 to 30 June 2024, using specific keywords and MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) terms in combination with the logical operators "AND" and "OR". The Google Scholar search engine has also been used for the manual selection of publications.
Results. The search identified 24 publications that were relevant to the topic under study and were included in the analysis. Studies in regulatory documents assessing the completeness, applicability and safety of information on the use of the drug in pregnancy (n = 3; 12.5 %) revealed a lack of sufficient data on people. Comparative studies of inconsistencies between different sources of information (n = 10; 41.7 %) showed inconsistencies between countries in the content of information on medicines produced by the same pharmaceutical companies, as well as differences between different sources of approved information. A number of studies (n = 5; 20.8 %) focus on current systems of risk classification in pregnancy, the effectiveness of prescribing information to warn of the teratogenicity of medicines and the adaptation of its content to the level of risk perception. In the United States, prescription information is divided into specific subsections, the content of which is regulated by the recently published Pregnancy and Lactation Labeling Rule, which was the focus of several studies (n = 6; 25.0 %).
Conclusion. The increasing use of medicines in pregnancy worldwide and the annual registration of new medicines, most of which contain limited or no safety information in pregnancy, support the relevance of this systematic review.
The article is devoted to the problem of safety of anticoagulant use in patients with burn injury against the background of polypharmacy. A retrospective analysis of 100 medical records of inpatients in the burn department who received anticoagulants for the prevention of venous thromboembolic complications (VTEC) was conducted for the period from 2022 to 2023, in order to study the safety of using anticoagulants in burn department patients with polypharmacy. According to the analyzed data, in patients taking anticoagulants in prophylactic doses and receiving more than 3 drugs simultaneously, in addition to changes in some clinical and laboratory parameters and coagulogram parameters (a significant increase in the number of blood leukocytes by 18 % (p ≤ 0.002), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) by 61 % (p ≤ 0.0001), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) by 32 % (p ≤ 0.0001), international normalized ratio (INR) by 11 % (p ≤ 0.02), activated partial thromboplastintime (APTT) by 7 % (p ≤ 0.0001), there is an increase in the length of the patient's hospital stay by 7 days (by 85 %, p ≤ 0.00003), compared with those who received less than 3 drugs.
Relevance. The incidence of cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasing worldwide, and the commonality and interrelation of their pathogenetic mechanisms determine the frequent development of comorbidity associated with high mortality rates, disability, and lower quality of life. The development of the most common chronic non-communicable diseases is based on oxidative stress, under which DNA damage occurs. In the last two decades, the relationship between DNA damage and the development and progression of metabolic disorders, cardiovascular lesions, and the possibility of using DNA damage as a biomarker have been actively studied.
Objective. Based on the analysis of currently available studies, to establish a relationship between the occurrence and accumulation of DNA damage with the development of comorbid pathology, including CVD and type 2 diabetes.
Methods. An analysis of Russian and foreign literary sources was conducted in databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, RSCI and eLibrary. It was decided to review studies assessing the association of DNA damage with MS, T2DM and CVD, and, based on the results obtained, to draw conclusions about the possible impact of comorbidity for these conditions on DNA structure.
Results. The results of the studies allow us to conclude that the development and progression of MS and associated T2DM and CVD are associated with the accumulation of high levels of DNA damage. It is important for comorbid patients with coronary heart disease and hypertension to consider the possible genotoxic effect of the prescribed drug therapy.
Conclusion. The studies presented in this review demonstrate a strong correlation of DNA damage determined by the DNA comet assay with metabolic disorders and markers of oxidative stress. The determination of DNA damage has prognostic value for comorbid patients and is a valuable biomarker that facilitates the early detection and treatment of combined cardiovascular and endocrine pathology.
PHARMACOVILIGANCE
Background. Fluoroquinolones continue to be widely used in the treatment of a wide range of infectious diseases, though new risks, including serious, have been identified in the process of their use. In order to maintain a favorable benefit-risk ratio, it is necessary to continue careful monitoring of the real-world safety profile of fluoroquinolones, which may allow, among other things, to develop new approaches to their rational use.
Objective. To study the structure of adverse reactions (ARs) associated with the use of fluoroquinolones based on a retrospective analysis of the national database of spontaneous reports.
Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis of spontaneous reports (SRs) received in the Russian database of ARs was carried out from 01.04.2019 to 28.02.2023. Inclusion criteria: SRs with ARs occurred on the territory of the Russian Federation, fluoroquinolone group drug indicated as a suspected drug (SD), identification of a high causal relationship "AR-SD". The Russian
version of MedDRA was used to code and systematize ARs.
Results. The study included 1890 SRs, out of them 950 were for levofloxacin, 633 for ciprofloxacin, 205 for moxifloxacin, and 102 for other fluoroquinolones. 75.5 % of the received SRs contained information about serious ARs, more than 80 % of ARs developed at the inpatient stage of medical care, self-medication was detected in 2.9 % of cases. 40.8 % of SRs included data on young people; patient age ≥ 75 years was indicated in 7.7 % of SRs; in 75 cases (4.0 %) fluoroquinolones were used in children under 18 years of age. The analysis showed that the most frequently reported ARs were from next 7 system-organ classes (SOC): skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders; gastrointestinal disorders; general disorders and administration site conditions; investigations; respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders, nervous system disorders and immune system disorders. In general, the proportion of these ADRs was 84.1 % with a variation in values in subgroups from 78.2 % for moxifloxacin to 91.9 % for ciprofloxacin.
Conclusion. The development of a set of measures to improve the general level of knowledge of physicians about the entire spectrum of ARs associated with fluoroquinolones is essential for the rational use of this group. It is necessary to identify not only common, but also clinically significant rare ARs of fluoroquinolones at early stages, and promptly send the information to Roszdravnadzor. Solving these problems will generally improve the safety of antibacterial therapy.
INTERNAL MEDICINE
Introduction. Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a clinical syndrome that is a widespread complication of cardiovascular diseases. The majority of patients with CHF are individuals with a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF ≥ 50 %). The number of such patients is increasing every year, while there is no effective drug therapy for this disease.
Objective. To create a portrait of a patient with CHF and analyze the 10-year survival rates on the Charlson Comorbidity Index scale in a cohort of patients, considering gender and age characteristics.
Materials and methods. Patients with CHF participated in the study. Demographic, anamnestic, and laboratory instrumental data were considered. The 10-year survival rate was assessed using the Charlson Comorbidity Index scale.
Results. The average age of the subjects was 62 ± 26 years. Among the pathologies of the cardiovascular system, hypertension prevailed — 274 people (100 %), angina pectoris — 184 people (67 %), and atrial fibrillation (AF) — 100 people (36 %). Among the studied 14 people. (5 % of patients) had a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), 8 people (3 %) had bronchial asthma (BA). 88 subjects (33 %) suffered a cardiovascular catastrophe. Among all the studies, the 10-year survival rate on the Charlson Comorbidity Index scale of less than 50 % was detected in 174 people (63.5 %), among whom 106 women predominated (39 %).
Conclusion. Portrait of a typical patient with CHF: male or female patient aged 60–69 years. Of the concomitant pathologies, most often those who are overweight / obese, hypertension, angina pectoris, atherosclerosis, AF, diabetes mellitus, who have had a history of myocardial infarction and/or stroke/transient ischemic attack. Older women (from 60 to 74 years old) are more likely to have a survival index of less than 50 % on the Charlson Comorbidity Index scale.
ISSN 2618-8473 (Online)