FROM EDITOR
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a multifactorial incurable immune-inflammatory disease. Progression leads to joint deformation, cartilage and bone tissue destruction, and subsequent disability. The primary goal of RA pharmacotherapy is to achieve disease remission. For this purpose, several classes of drugs are used: basic anti-inflammatory drugs (DMARDs), which are a large group of synthetic and biological drugs that are combined according to their ability to influence the pathogenetic mechanisms of RA; glucocorticoids, which are recommended for use in combination with DMARDs; and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are used to relieve acute and chronic pain. The treatment of RA is a long-term process, and the drugs used for this condition are not always safe and not always effective, which leads to discontinuation of treatment in 20–50 % of patients. Therefore, there is a need to develop new pharmacological targets that can increase drug effectiveness and reduce drug toxicity. One promising therapeutic target is proteinase-activated receptors (PARs), particularly PAR2, whose activation contributes to the occurrence of inflammation, fibrosis, and proliferation of connective tissue. Experiments have demonstrated that inhibition of PAR2 activity prevents the development of RA pathogenesis and positively modifies the course of the disease. The search for drugs that inhibit PAR2 was carried out in the following directions: indirect blockade of PAR2 activity; creation of monoclonal antibodies; search for PAR2 inhibitors among peptide compounds; synthesis of low-molecular-weight inhibitory substances.
Relevance. Acne is one of the most common dermatological diseases, affecting a significant proportion of the population, particularly adolescents and young adults. The modern pharmaceutical market offers several drugs for acne treatment, including topical retinoids, antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid, as well as systemic drugs, such as isotretinoin and hormonal agents. The growing problem of antibiotic resistance among microorganisms, including Propionibacterium acnes, requires rational antibacterial drug use and alternative acne treatment methods.
Objective. A comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of various methods of acne drug therapy to optimize treatment approaches and improve therapy results.
Methods. As part of this review study, a comprehensive analysis of the scientific literature on acne drug therapy was conducted. The inclusion criteria were original studies, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews published over the past 5 years (2018–2023).
Results. An analysis of the literature has shown that topical retinoids and antibiotics, as well as systemic retinoids and antibiotics, remain the most effective methods of treating acne.
Conclusion. The analysis of the modern scientific literature confirms the effectiveness of existing methods of drug therapy for acne. The choice of optimal therapy should be based on the individual characteristics of the patient, the severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant factors.
DRUG SAFETY
The authors developed a methodology for an in-depth study of the safety of pharmacotherapy based on a quantitative integrated analysis of adverse events in the context of clinical trials. The methodology was tested using data obtained during a bioequivalence study of trastuzumab.
Objective. Practical implementation of the approaches developed by the authors for the individualized assessment of safety of pharmacotherapy based on quantitative integral analysis of adverse events.
Materials and methods. This five-step algorithm modifies information regarding registered adverse events during clinical trials. Subsequent integral assessment of adverse drug events, in which each event is assigned a certain score and weighting coefficient, followed by aggregation of data to obtain an integral indicator at the system-organ and organism levels.
Conclusions. The algorithms proposed by the authors of the article for a systematic analysis of adverse events associated with the use of trastuzumab allow us to predict the safety of prescribed pharmacotherapy and, in the future, move to a risk-based approach when using this drug at the post-registration stage.
Relevance. Pharmacotherapy during pregnancy is associated with great risks for the fetus in the case of therapy of non-obstetric diseases of the mother, in addition, issues of improving the effectiveness of treatment of placental pathology, thrombophilic conditions, and other pregnancy complications remain a priority. Recently, the possibilities of using nanomaterials in medicine have been actively studied, including for the purpose of modifying the delivery or distribution of medicines.
Objective. The aim was to conduct a structured analysis of the published literature on the use of nanomaterials for therapeutic purposes during pregnancy.
Methods. The analysis of publications in PubMed, Cyberleninka, and eLIBRARY databases on the keywords “Nanoparticles” and “Pregnancy” was carried out, with the exception of mentioning nanoparticles in the context of environmental pollutants, as well as in the context of diagnostic methods.
Results. Information is provided on the nature of nanoparticles that have been developed and studied in the context of the prospect of use during pregnancy. An overview of the areas of clinical application of such materials is provided, as well as the available evidence of their effectiveness and safety.
Conclusion. Therapeutic systems containing drugs and various nanomaterials have a good potential for clinical use in order to ensure targeted drug delivery, modification of their bio-distribution in order to increase clinical efficacy and reduce the toxicity of drugs.
PHARMACOECONOMICS
Relevance. Chronic cerebral ischemia is a collective term describing various brain vascular lesions that develop without a stroke. For neuroprotective action and correction of cognitive impairment by acting on AMPA receptors, calcium salt of N- (5-hydroxynicotinoyl) — L-glutamic acid was synthesized. The effectiveness and safety of these drugs were initially demonstrated in biological models and were further confirmed in patients with chronic cerebral circulatory disorders.
Objective. To determine the optimal drug therapy for patients with chronic cerebral circulatory disorders on the basis of a comprehensive pharmacoeconomic analysis using the methods of analysis "cost of disease", "cost-effectiveness" and "cost-utility".
Materials and methods. Results of a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the efficacy and safety of calcium hydroxynicotinoyl glutamate (phase III); the results of studies on the effectiveness of ethylmethylhydroxypyridinesuccinate.
Results. According to the analysis the cost of the disease, "cost-effectiveness", "cost-utility" in patients with chronic cerebral circulatory disorders, it is more economically feasible to prescribe the drug calcium hydroxynicotinoyl glutamate.
Conclusions. According to the results of the study, the economic aspects of the rational use of health resources, as well as pharmacoeconomic parameters that determine the choice of tactics for the treatment of patients with chronic cerebral circulatory disorders, are of great importance.
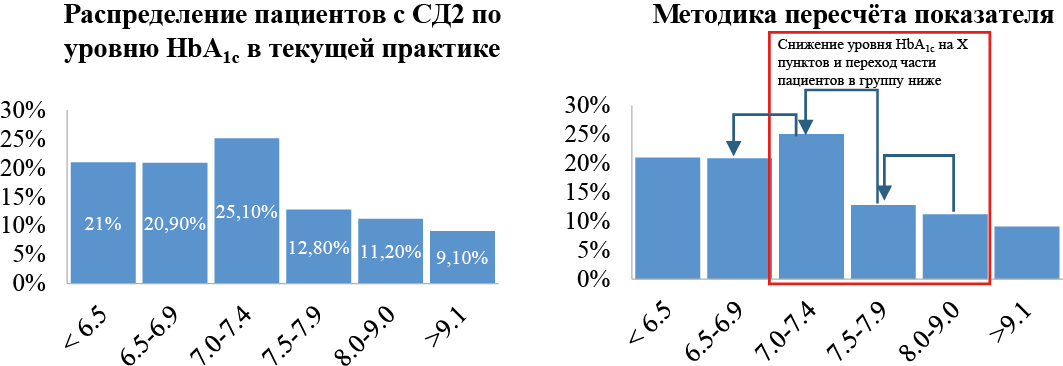
Background. Since 2023, Russia has been implementing the Federal Project "Fight against diabetes mellitus" with a key objective of increasing the proportion of patients achieving a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level below 7.0 %.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the contribution of expanding the use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (iDPP-4) (in the example of evogliptin) in achieving the targets of the Federal Project "Fight against diabetes mellitus" and reduce mortality, as well as the budget impact analysis of such policies.
Materials and methods. The target population of the study were adult patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) whose HbA1c levels ranged from 7.1 % to 9.0 % while on glucose-lowering therapy with metformin (MET), sulfonylureas, or their combinations, and with the absence of significant comorbidities (e. g., ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular diseases, myocardial infarction, or diabetic nephropathy). We also included patients receiving a combination of MET and Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 inhibitors. To assess the change in HbA1c levels when evogliptin is included in the treatment regimen, a mathematical model was developed based on data from the Federal register of diabetes mellitus, clinical studies on the use of iDPP-4, and expert consultations. To model mortality, we incorporated evidence from meta-analyses demonstrating that exceeding target HbA1c levels are associated with higher mortality. Only the costs of antidiabetic therapy were considered expenses. The budget impact was defined as the difference between the costs within the current treatment practices for DM2 in the study patient cohort and the expected expenses when modifying the therapeutic approach.
Results. The target population of patients who can be prescribed evogliptin in addition to existing hypoglycemic therapy is 937,225 people. Expanding the use of evogliptin in patients from the target population can reduce mortality by 851 cases in the first year and save up to 4,275 lives of patients with type 2 diabetes over a 5-year horizon. In addition, this will allow us to exceed the goal of the Federal Project "Fight against diabetes" within one year for the proportion of patients with diabetes with a glycated hemoglobin level of 7 % or less, increasing the figure to 52 % (with a target value of 42.39 %).
Conclusion. Expanding the use of evogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes will help achieve the target indicators of the Federal Program "Fight against diabetes mellitus" and reducing population mortality.
DRUGS UTILIZATION RESEARCH
Adherence is one of the crucial determinants of high-quality and effective pharmacotherapy. Along with the search for optimal methods to improve adherence and with the study of factors influencing it, it remains an equally urgent task to choose the optimal method to evaluate it. In the context of the digitalization of healthcare systems that is actively taking place in many countries, including Russia, the approach based on the analysis of prescription data is of the greatest interest among all known methods of measuring adherence. The calculation of the «proportion of days covered» (PDC) has become the most widespread among the variants of this approach. However, the local adoption of foreign experience of assessing adherence by PDC turned out to be hampered by the presence of significant problems associated with insufficient standardization of the calculation methodology and interpreting the results obtained. The purpose of this work was to develop the standard PDC calculation method based on the EMIAS prescription claims data to increase compliance with the requirements for qualitative studies of medication adherence. The analysis of the literature made it possible to identify and describe the following most significant elements of PDC calculation methodology: (1) minimum fill criterion; (2) evaluation period; (3) method for identifying fill date; (4) calculation of the total number of days in the evaluation period; (5) calculation of the number of days covered with prescriptions; (6) interpretation of PDC calculation results; (7) assessment of multiple adherences. Based on the results of the literature analysis and on the experience of conducted pilot study, in the summary of this paper, an optimal list of recommendations was presented that allows for a qualitative assessment of adherence by PDC methodology.
ORPHAN DRUGS
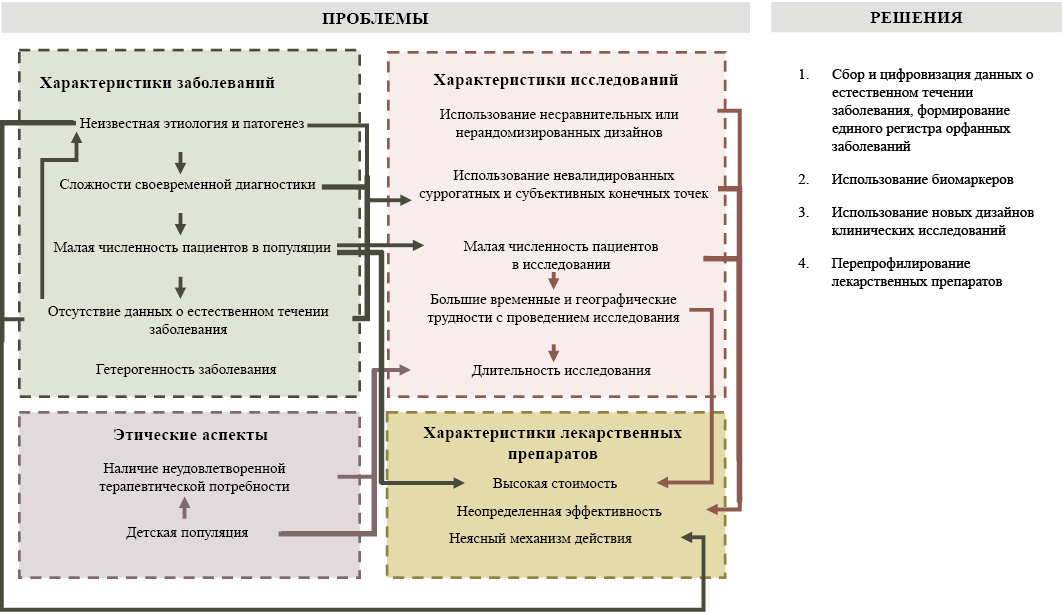
Medicinal products (MPs) for treating rare (orphan) diseases are characterized by high uncertainty regarding clinical efficacy. This uncertainty is primarily attributed to the limited number of available and completed clinical trials and inconclusive data on efficacy. The purpose of this review was to describe the main issues related to the characteristics of orphan diseases, including the characteristics of clinical trials of orphan MPs, the orphan medicines themselves, ethical issues, and suggestions for possible solutions to these problems. This review identified and described the main aspects affecting the diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases, development of orphan MPs, and quality of clinical trials. In addition, issues related to quality of life were considered.
Furthermore, some organizational and clinical solutions were suggested to reduce the uncertainty of the utilization of orphan MPs, allowing for greater clarity in their implementation in practice.
PROVISION OF DRUGS
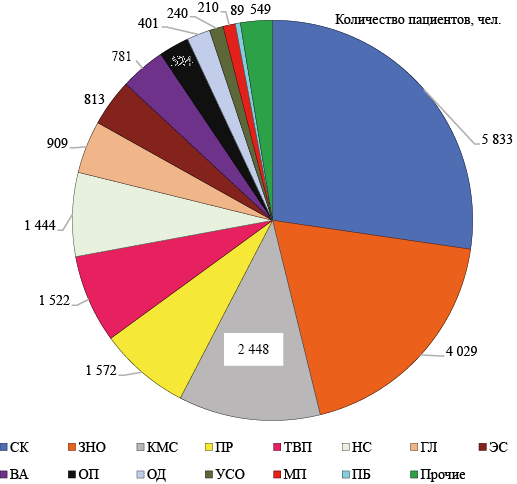
The most important component of the rational use of medicines in the preferential medicinal segment is the purchase of medicines based on patient nosological analysis.
Objective. To investigate the compliance of medicinal provision with the structure of diseases of patients receiving pharmacotherapy under the Program for providing certain categories of citizens with necessary medicines (Program) and develop recommendations for improvement.
Materials and methods. A nosological analysis of 463 forms of medical and social expertise in 125,234 patients, an ABC/VEN-analysis of the nomenclature of medicines purchased for the Program over a 3-year period, and an assessment of rational medicinal use using descriptive statistics methods were carried out.
Results. A significant discrepancy was observed between the number of patients in the disease groups and the volume of funding for medicines. Less money is spent on purchasing medicines for the treatment of diseases that occupy leading positions in terms of the number of patients, — cardiovascular diseases and malignant neoplasms, than on medicines for the treatment of other diseases that affect a smaller number of patients.
Conclusions. There is a discrepancy between the medicinal supply and the structure of patients’ diseases, which is due to irrational planning of the range of purchased medicines, and requires correction.
INTERNAL MEDICINE
Changes in body composition: sarcopenia and obesity are common in patients with chronic heart failure, complicating the disease course and worsening the prognosis.
Objective. To investigate the effectiveness of the proposed rehabilitation method, which consisted of a combination of a hypocaloric but high-protein diet, individualized physical activity, and breathing exercises.
Materials and methods. Patients (n = 80) were divided into 2 groups depending on the presence of sarcopenic obesity. In each group, the main and control subgroups were distinguished depending on the inclusion of the rehabilitation program in the management tactics. Changes in the muscle component of body composition and quality of life were assessed using the Minnesota questionnaire.
Results. Both groups exhibited significant improvements in body composition parameters and quality of life.
Conclusion. The rehabilitation program was effective in patients with and without sarcopenic obesity in terms of improving the muscle component of body composition and quality of life.
EDUCATION
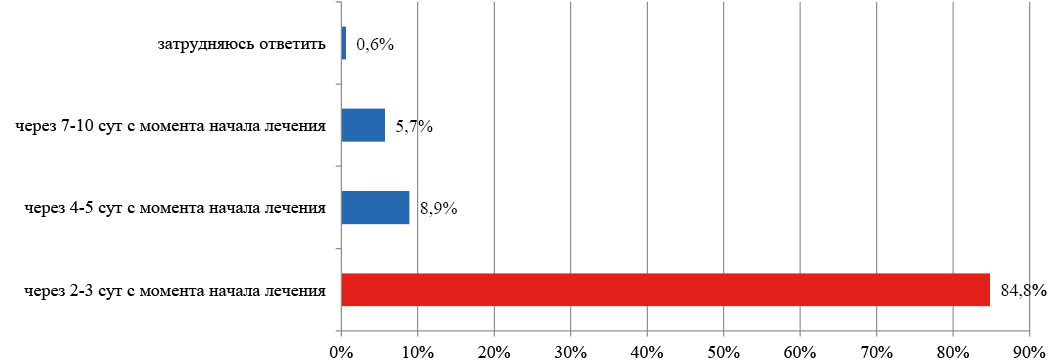
Relevance. In the context of the continuing growth of antibiotic resistance, an important aspect of antimicrobial drug use is increasing the knowledge level of medical university students regarding the main issues of rational antimicrobial therapy.
Objective. To determine the level of basic knowledge of 6th year students at the Institute of Clinical Medicine (ICM) on the main issues of the rational use of antimicrobial drugs (AMD).
Materials and methods. The data from an anonymous survey among the 6th year students of the ICM, carried out in the 2023–2024 academic year were analyzed.
The results are presented in the form of an "average percentage of responses to a question" (APR). The best results were shown by the student who answered the following questions: the time to evaluate the effectiveness of initial antimicrobial therapy in (AMT) (APR = 85 %), the need to replace AMD with a positive clinical effect (APR = 60 %), and tactics for the treatment of acute tonsillitis/pharyngitis (APR = 56 %). The worst results were shown by the students answering the following questions: combination of AMD (APR = 16 %), criteria for AMD withdrawal (APR = 18 %), auxiliary drugs for bacterial infections of the respiratory tract (APR = 8 %), the choice of first-line AMD for mild community-acquired pneumonia (APR = 18 %), acute cystitis (APR = 17 %), acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis (APR = 7 %), the choice of a rational administration schedule of ampicillin (APR = 29 %) and cefixime (APR = 33 %).
Conclusion. Based on the results of the survey, it can be concluded that there is an insufficient knowledge level of basic AMT issues among the 6th year ICM students (on average, 37 % of correct answers in the questionnaire as a whole).
ISSN 2618-8473 (Online)